News & Events
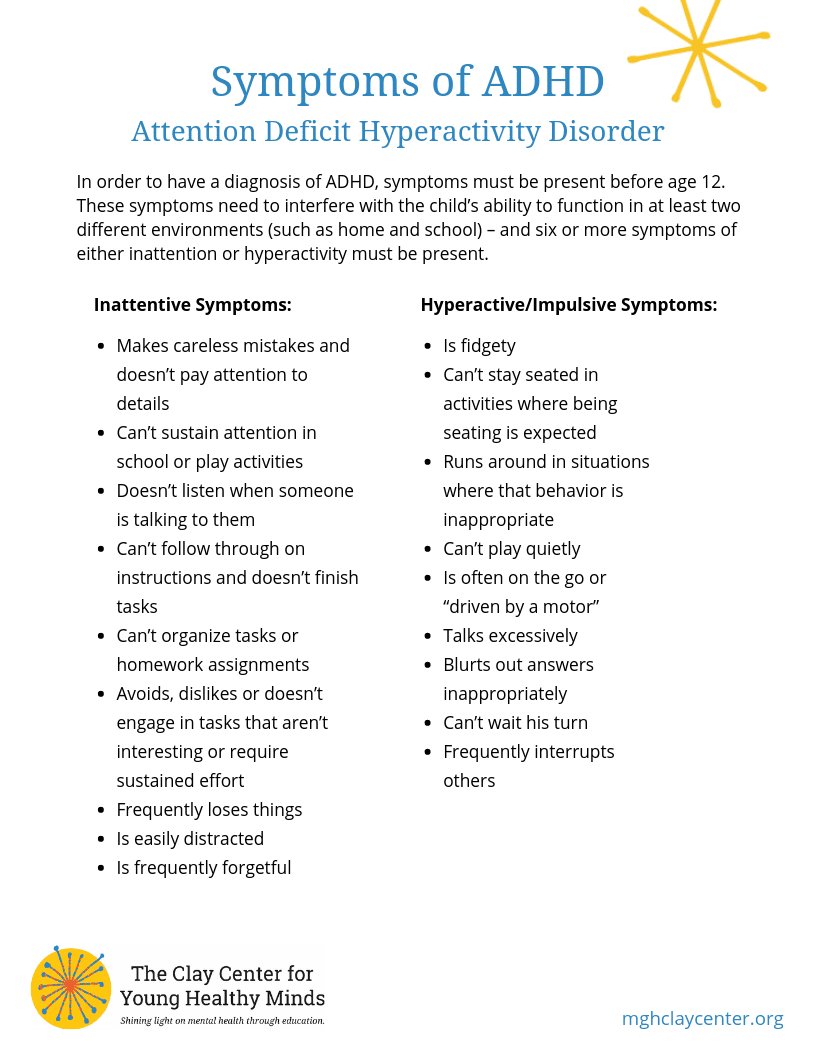
In order to have a diagnosis of ADHD, symptoms must be present before age 12. These symptoms need to interfere with the child’s ability to function in at least two different environments (such as home and school) – and six or more symptoms of either inattention or hyperactivity must be present.
Inattentive Symptoms:
Makes careless mistakes and doesn’t pay attention to details
Can’t sustain attention in school or play activities
Doesn’t listen when someone is talking to them
Can’t follow through on instructions and doesn’t finish tasks
Can’t organize tasks or homework assignments
Avoids, dislikes or doesn’t engage in tasks that aren’t interesting or require sustained effort
Frequently loses things
Is easily distracted
Is frequently forgetful
Hyperactive/Impulsive Symptoms:
Is fidgety
Can’t stay seated in activities where being seating is expected
Runs around in situations where that behavior is inappropriate
Can’t play quietly
Is often on the go or “driven by a motor”
Talks excessively
Blurts out answers inappropriately
Can’t wait his turn
Frequently interrupts others